We have installed a heat recovery system in a restaurant along with a ventilation system with variable air flow on request. A run-around coil type air-to-air heat recovery system was selected. The warm water obtained from the heat recovery coil was distributed to three separate coils. The first serpentine is the preheating serpentine for the kitchen hoods, the second serpentine dining room the fresh air air conditioning units, the preheating serpentine for the kitchen and the third serpentine office and personnel rooms are the preheating serpentine for the split air conditioner.
Temperatures were monitored and recorded during 2014-2015 winter months. Although there was no second heating coil in the air conditioner in the kitchen fresh air, there was no discomfort.
Application
For Ankara, the outside temperature for winter is -12 ° C. The outdoor temperature for summer is 34 ° C, and 18 ° C. At these temperatures, evaporative cooling in Ankara gives good results.
In Ankara, a ventilation system was installed using heat recovery, student-dependent speed control and transfer air in a restaurant kitchen. Evaporative cooling module is added on the air conditioner of fresh air.
The two main hoods (one on the barbecue grill, the other on the open hearth) and the other small hoods were assembled in a single exhaust system.
Exhaust ducts are used to protect the exhaust air temperature and to prevent oil and soot accumulation on the inner wall of the duct. It was isolated with 25 mm thick stone wool.
Total exhaust hood exhaust at full load is calculated as 15,000 m3 / h. Combovento 2 × 75/175 HR model device was used. An automatic washing system has been established to protect the efficiency of electrostatic filtration. The hot water obtained from the heat recovery coil is distributed to fresh air devices by an in-line pump. For the fresh air supply of the restaurant, three different devices and channel lines were created. The exhaust fan and the kitchen fresh air are driven by the air conditioner fan frequency converters.
One of the three appliances that gives fresh air to the restaurant is the air conditioning unit that feeds the kitchen fresh air. This air handling unit with 10,000 m3 / h of 100% outside air contains a heating coil and an evaporative cooling cell. The kitchen fresh air heats the fresh air in the winter months with the hot water obtained from the heat recovery coils of the A / C unit exhaust side. Kitchen fresh air does not have a second heating coil in the air handling unit. The fan of the kitchen fresh air power plant is driven by a frequency converter. Kitchen fresh air hood 30 cm below the lower level. At a rate of 0.45 m / s above.
The second fresh air serves the dining hall of the air handling unit. This air handling unit with a capacity of 10.000 m3 / h is receiving 50% of 5,000 m3 / h fresh air. Exhausted from the dining room, 5,000 m3 / h of fresh air is taken from the kitchen-hall door to the kitchen as a transfer air and the dining room is kept at a positive pressure. In fresh air, air conditioning system heat recovery is done by the heated water that comes from heat recovery serpentines.
The third fresh-air device is a split-type air conditioner with a channel that serves office and staff rooms. The air flow of the split air conditioner is 3,000 m3 / h. 2.000 m3 / h fresh air is taken from outside and 1,000 m3 / h return air is used. Some of the hot water from the heat recovery coil in the exhaust line was used to warm the fresh air in winter with a preheater coil placed in front of this split air conditioner. The air temperature at the outlet of this serpentine is not measured nor monitored. But the fact that the split air conditioner can operate with 70% fresh air even on the coldest days during the whole winter shows that the air from the preheater coil provides the desired air flow.
The hood exhaust fan and the kitchen fresh air handling unit fan are controlled by common control voltage with different frequency converters. Employees who adjust the exhaust valve according to exhaust requirements in the hood automatically adjust the amount of fresh air. After the common control voltage is processed in a DDC, the fresh air, air conditioner operates the frequency converter.
Results
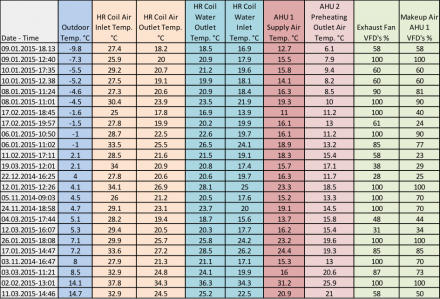
The temperatures before and after the outside air temperature, the exhaust air heat recovery coil, the heat recovery coil inlet and outlet temperatures of the circulating water in the heat recovery circuit, the air outlet temperatures of the fresh air conditioning units and the control voltages of the frequency converters were measured and recorded. The measured values are given in the table below. For convenience of comparison, values are listed according to the outside temperature.
Table-1 lists the values at the time when the kitchen fresh air air-conditioning unit and hood exhaust fan frequency converter voltages are multiplied by constant coefficients.
It has been tried to provide many different multiplier pressure balances.
Table-2 lists the values at the time when constant coefficients are not used when the kitchen fresh air, air handling unit and extractor exhaust fan are multiplied by different coefficients at different times.
Reviews
When the values in Table 1 are examined, fluctuations are seen. When we look at the flow rate and temperature differences, it seems that more heating has been done from the heat recovery. This can be caused by two reasons: 1 – There must be some hidden heat gain in the heat recovery coil, 2 – Fresh air is lower than project values. Indeed, according to the partial loads, the fresh air conditioner has pressure imbalances at full load when the fan cycle is set and partial loads when set at full load. At different speeds, the balance between the fresh air fan and the exhaust fan is not parallel because the exhaust fan reactions aren’t going parallel.
Table 2 shows the values obtained by driving the fresh air fan control voltage at different ratios. The fresh air fan is driven at different ratios according to the exhaust fan at different ratios, the average factors are used in the intermediate values. At full load, the fresh air frequency converter exhaust fan voltage is multiplied by 0,83, at partial load multiplication get even closer to 1 and as can be seen from the table even surpasses it.
After the frequency converter control voltage is set to this, indoor, outdoor air becomes balanced with the air flow of the restaurant and the heat recovery values and fresh air heating values start to overlap each other.
When unmeasured split air conditioner preheater is taken into account, a hidden heat gain is noticed. This result also overlaps with the serpentine selection outputs. In the serpentine election output, there is also some condensation in the heat recovery coil and it seems to be a hidden heat gain.
Despite the fluctuations, Table-1 has an interesting conclusion. One of the assumptions that can be made before measurements is that the fresh air will increase in the serpentine exit temperatures in some load segments. Because the airflow would fall, the serpentine output temperature would increase. But in the case of partial exhausts, the temperatures of fresh air blowing at the same exhaust air temperatures were also the same. In fact, this result coincides with the serpentine election output. Serpentine capacities also decrease as the air flow over the serpentine drops. Even though the air temperatures are the same, the amount of heat obtained is reduced.
The lowest kitchen fresh air blowing temperature was 11 ° C. The exhaust air temperature was assumed to be 40 ° C. The exhaust air temperature has never risen to 40 ° C and the design target of 16 ° C, the lowest fresh air blowing temperature, has not been achieved. The realized 11 ° C and the design target of 16 ° C are below the comfort blowing temperature values. However, since the blowing air is delivered at very low speeds and the hoods are located in front of the hood, some of the cold air is drawn by the hoods without falling to the human working height. The speed of fresh air given to the hood at very low speeds at full load has fallen to very low values at partial loads. The air circulating at the employees level is also mixed with the transfer air coming from the dining hall, so comfort conditions are provided for the employees.
As we have already mentioned, it is satisfactory that split air conditioner is able to work with 70% fresh air in Ankara during winter months and this target has been achieved.
The rate of oil and soot accumulation in the channel inner walls is very low. The low in-duct speeds in the partial loads did not increase the accumulation. Possibly the heat insulation of the canal has had a positive effect.
No additional heating has been applied to the heating of the kitchen fresh air by using 3 systems (heat recovery, arbitrary control and transfer air usage) required in the ECSR Standard 92.1. The system, which is very useful in terms of operating costs, also reduced the investment costs. A total of 100 kW capacity condensed wall type boiler and saloon type air conditioner final heater were used for preparing boiler hot water.
Although it is not given in the charts, it is useful to give it as additional information. In the summer, evaporative cooling allowed kitchen fresh air blowing temperature to be 10 ° C lower than outdoor air temperature. Due to the high air circulation, there is no excessive humidity in the kitchen. Evaporative cooling has not kept the comfort of mechanical cooling. Nevertheless, when compared to investment and operating costs, this study has been very useful for the kitchen.
